The ear forms the bodies of balance and hearing . Also called cochlear vestibular organ in the study of medical sciences .
Overall the study histoanatómico ear is divided into three parts, outer ear, middle ear and inner ear .
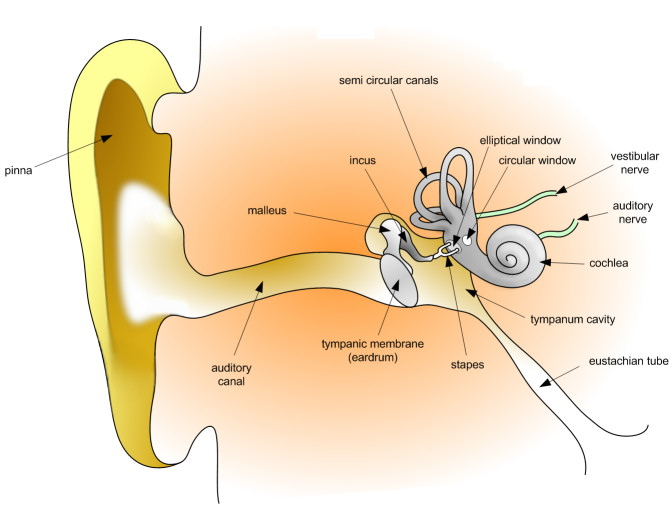
External ear
was originally composed by Pinna and external auditory canal.
The auricle is covered by elastic cartilage covered with soft skin and that skin has abundant oil glands, known as drink hairiness , and in most medial cartilage architecture possesses fibers muscle striatum that communicate with the external ear canal, giving strength and support as well as some capacity for movement in humans. Animal in the ear can be seen in the study of the vestibulocochlear organ mammals terrestrial extrinsic muscles of the ear.
The external auditory canal extends from the flag to the eardrum . This meatus or through measures at an average of about 3.5 cm long in humans, and can measure up to 7 cm in other mammals . It consists of cartilage elastic, bone and soft skin. Also presented drink villi are certainly more abundant in male subjects. Just skin glands are located ceruminous, which are a kind of apocrine sweat glands, being responsible for the production of earwax, which are designed to protect the ear cavity of foreign agents, such as dust , parasitic agents , virulent agents and certain bacterial agents , and avoid maceration of the soft skin of the meatus or canal.
Middle Ear
be seen within its architecture anatomical : tympanic cavity, tympanic membrane, the osteocillos otic (ear bones), sinuses and mastoid cells and the pharyngeal tuba (formerly Trunk Eustaquio ).
Within the tympanic cavity is comprised an irregular heart full of air, this element comes from the nasopharynx through of pharyngeal tuba, and is responsible for coupling to the structure intratympanic as well as serve as a means of transporting acoustic frequencies. The tympanic cavity is covered by a tunica mucosa and epithelial layer simple flat type on the back, but the former is seen a epithelium pseudostratified cylindric ciliated type with abundant cells goblet.
The tympanic membrane is transparent aspect separates the tympanic cavity of the outer ear canal. Ovaloide has a structure with an average diameter of about 1 cm. A tympanic membrane was studied two parts, the Pars Tensis or grooved portion and Pars laxus or portion lax. It consists of three layers:
- stratum corneum : is skin covering the outer surface of the tympanic membrane, lack of hairs and glands, composed of epidermis rests on a layer of connective tissue subepidermiana.
- Mucosa : Of the inner surface of the intermediate layer of connective tissue, with a epithelium simple flat features.
The otic osteocillos three tiny osteocillos are labeled by their anatomical architecture with the name of the Martelus (Hammer) the Anvilus (Yunque) the Lenticulens (Lenticular) , and Estribalis (bracket) . The stirrup is the smallest bone in the human body. These form a chain that extends from the tympanic membrane to the window ovaloide. The osteocillos are composed of compact bone tissue cartilage hyaline. The role of osteocillos otic and the tympanic membrane is the transformation of sound waves traveling through the air in the tympanic cavity to sound waves traveling through the ear perilymph procedure. When sound waves enter the middle ear, the hammer hits the anvil and this hitting the bracket immediately, after this process the sound passes through the oval window and circular window . The tuba pharyngeal or eustachian tube measured in adult humans of about 4 cm on average. It consists of a bony and a cartilaginous, has an epithelial layer composed of epithelium rhinopharyngeal or pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with abundant goblet cells. Serves to equalize pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
Inner ear
Labyrinthus also called, is divided in turn into Labyrinthus Osseus (bone) and Labyrinthus captivus (membranous). In Labyrinthus Osseus the semicircular ducts belong to the body's own balance, while the coclearis or shell belongs to the organ hearing. The Labyrinthus Osseus contains a fluid called lymph perilymph which is located in the perilymphatic space.
The laberintus captivus is subdivided into Labyrinthus vestibularis and Labyrinthus coclearis . The Labyrinthus vestibularis includes estatoconios saculus called utriculus and located in the bony semicircular ducts. The Labyrinthus coclearis comprises the coclearis canaliculus bone located in the cochlea. The Organ of Corti is located in the canaliculus coclearis and is called the receptor organ for hearing and proprioception .
There also are three semicircular canals in semicircles arched tubes implanted into the lobby and located three rectangular planes, according to the three dimensions of space. The semicircular canals provide us with the notion of space and, therefore, contribute to maintaining the balance of the head and body.
Then we found the cochlea is a coiled tubing system with three different tubes, one beside the other so-called scala vestibuli, scala media and scala tympani. The scala vestibuli and media are separated by the vestibular membrane (MV), the scala tympani and the scala media are separated by the basilar membrane (MB). On the surface of the basilar membrane is a structure, the organ of Corti, which contains a series of mechanically sensitive cells, hair cells. The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with perilymph, it is rich in Na and poor proteins . The scala media contains endolymph which is rich in protein and contains mostly K . The scala vestibuli is related to the oval window through the lobby and the scala tympani is bounded by the round window. Both ducts communicate openly at the apex of the snail or helicotrema. The hair cells supported by Deiters cells are arranged angularly and ends reach the jelly-like tectorial membrane and that is spread over the hair cells.
The vestibular membrane is so thin, that does not hinder the passage of sound vibrations from the scala vestibuli to the scala media. Therefore in terms of transmission sound , the scala vestibuli and a half is considered as a single camera. The importance of the membrane depends on preserved vestibular endolymph in the scala media necessary for normal functioning hair cells.
corti Body
is the key organ of proprioception auditory processing in general. It is also named as organ or body spira spiral as found throughout the course of the cochlear duct, located in the inner ear. Consists of a thickened epithelium of features too complex, impossible to define even under electron microscopy , but their study can be summarized in two cell sources:
- cochlear hair cells : Their function is to transform physical beep beep cortilinfáticas mechanical and electrochemical signals of such a receiving area designed to auditory cortex.
-
- outer hair cells, are located on the periphery of outer columnar cells forming 4 regular rows with an approximate number of 13.000 cells. His nerve endings are afferent and efferent characteristics.
- : Sostentaculocitos differentiated resting on a basement membrane, there are 6 types referred to by their microstructure:
- internal limiting Cells: prepares the Nuel space of the middle tunnel.
- inner phalangeal cells: Provide maintains a pillar.
- internal columnar cells: design the tunnel of Corti tunnel procedure.
- external columnar cells: design the tunnel of Corti tunnel procedure.
- phalangeal cells provide an external supports pillar.
- cells external constraints: They make the space of Nuel and tunnel environment.
tunnel of Corti and Nuel space called cortilinfa, acoustic-receptor function
0 comments:
Post a Comment